Plant exosomes: tiny vesicles with a big impact on skin care
Introduction
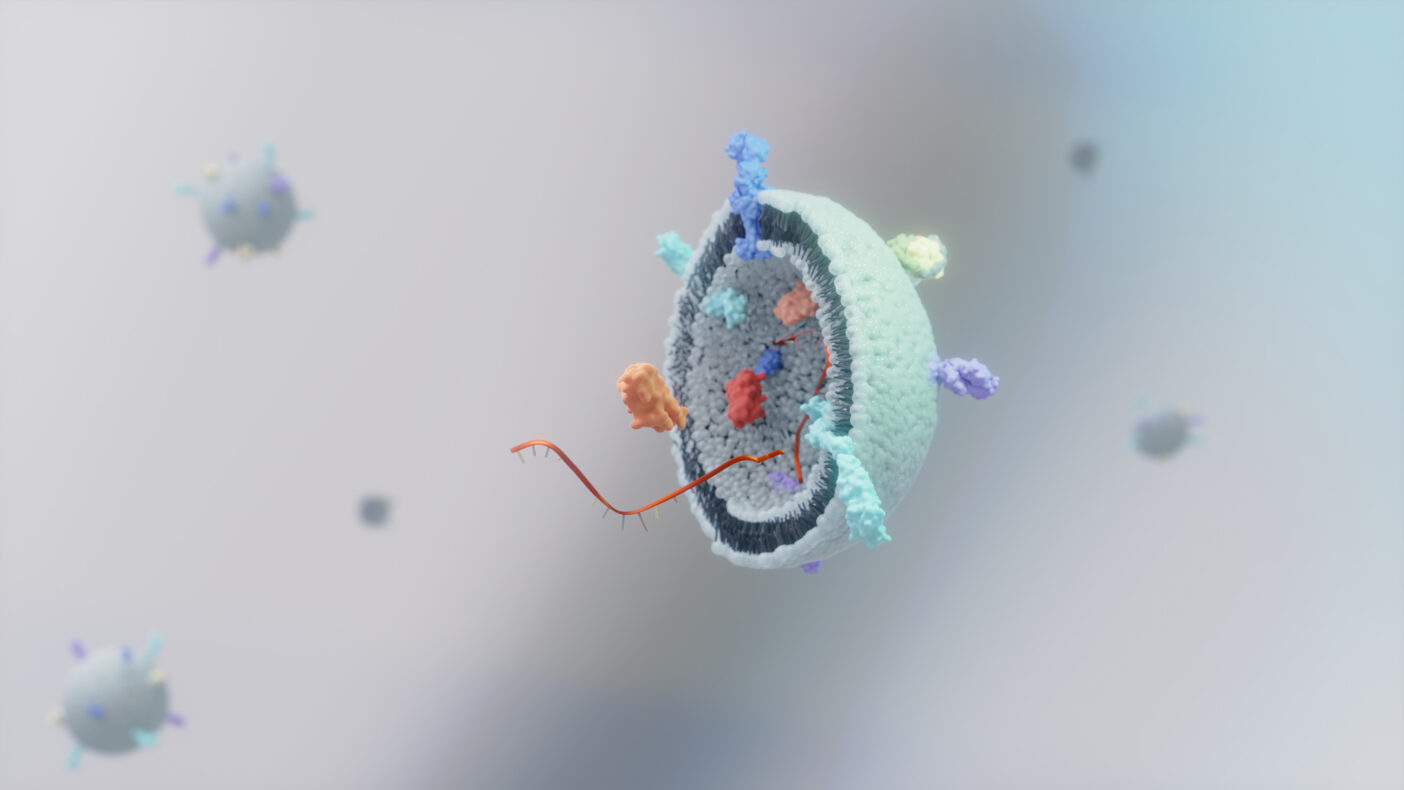
When people talk about high-tech skin care these days, one term is cropping up more and more often: plant exosomes. Exosomes are tiny vesicles that are released by cells to transport messages. They are comparable to microscopic packets filled with proteins, lipids and genetic information. In skin care, these nano-postmen are used to deliver active ingredients deeper, more precisely and more gently to where they are needed. No wonder, then, that cosmetic products containing exosomes are considered the next big trend in anti-ageing serums, repair ampoules and after-treatment care. But what is really behind them? How are exosomes formed, where do they occur in nature and what can they do for, on and in our skin? This blog article answers these questions in an understandable, practical and scientifically sound way and shows why cosmetic products containing exosomes are currently conquering the beauty shelves.
Occurrence in nature
Exosomes are found in almost every living organism. Animal and plant cells release them to exchange information. Plant exosomes are particularly exciting for cosmetics because they do not contain any animal components and are therefore vegan-friendly.
These plants form exosomes from their cell membranes. The tiny vesicles contain secondary plant substances such as polyphenols and vitamins. These can be incorporated into cosmetic products to deliver antioxidant or anti-inflammatory effects exactly where they are needed.
Extraction and purification
For cosmetic products containing exosomes, these must first be isolated from plant or animal-free cell cultures. This is usually done in four steps:
- Cultivation: The starting cells grow in sterile bioreactors.
- Separation: Exosomes are separated from other cell components by ultracentrifugation, membrane filtration or microfluidics.
- Purification: Multi-stage washing and dialysis processes remove proteins or lipids that do not belong in the finished formulation.
- Stabilisation: Freeze-drying or lipid coating protects the sensitive nano-vesicles from oxidation.
It is important to keep the temperature below 4 °C, neutralise the pH value and work under sterile conditions – only then do the exosomes remain biologically active and safe for use in cosmetic products.
Advantages and disadvantages of plant exosomes
Advantages
- Targeted transport of active ingredients: Exosomes fuse with the cell membrane of our skin, allowing antioxidants, peptides or growth factors to penetrate deeply.
- High bioavailability: Because exosomes are similar to the body’s own vesicles, they are hardly rejected.
- Multifunctionality: A single exosome can carry several active ingredients – ideal for complex formulas.
Disadvantages
- Regulatory grey area: In Europe, human- or animal-cell-based exosomes are currently not permitted to be sold as cosmetic products. Plant exosomes are permitted, but require an official INCI entry.
- Complex production: Ultracentrifuges and clean room technology drive up the price.
- Stability: Without suitable encapsulation, exosomes can lose their activity within a few weeks at room temperature.
Nevertheless, more and more manufacturers are turning to cosmetic products containing exosomes because the benefits outweigh the obstacles – especially when plant sources are used.
Areas of application in cosmetics and everyday life
- Anti-ageing serums: repair of the skin barrier, reduction of wrinkles, increase in collagen synthesis.
- Post-procedure care: after microneedling or laser treatments, exosomes soothe the skin and accelerate regeneration.
- Hyperpigmentation treatments: Inhibition of tyrosinase by plant polyphenols in exosomes.
- Moisturising masks: Exosomes from aloe vera or cucumber provide natural moisturising factors.
- Daily body care: Lotions with rice exosomes improve the elasticity and smoothness of the skin.
Brands such as ‘EXO|E™ Revitalising Serum’ and ‘DP Derm Exo-Skin’ demonstrate how exosomes are already being successfully marketed in cosmetic products. Exosomes are also finding their way into hair care products, lip care and eye patches.
Plant Exosome fact sheet
- Appearance: milky-clear suspension of nano-sized vesicles (30–150 nm)
- Molecular composition: lipid bilayer, proteins (e.g. tetraspanins CD9, CD63), RNA, microscopic signal peptides
- Aggregation state: colloidal solution
- Melting point: not defined, as the lipid membrane liquefies at > 37 °C.
- Solubility: dispersible in aqueous buffers or hyaluronic acid gels, insoluble in oil
- INCI name: ‘Vesicles’
- Synonyms: extracellular vesicles, nano-vesicles, EVs
However, we only accept plant exosomes that are also listed as ‘vesicles’ in the INCI! Due to the hype surrounding exosomes, many suppliers of plant extracts believe that they can now simply sell their existing extracts at a high price under the “exosome” banner.
We do not accept this and therefore only use ‘genuine’ exosome active ingredients.
Relevant cosmetic plant exosome ingredients
| Name | Company Name | INCI Name | Remark |
|---|---|---|---|
| HEARTLEAF EXOSOME™ | GSI Europe - Import + Export GmbH | Houttuynia Cordata Vesicles , aqua , Glycerin , Pentylene Glycol | |
| CICA EXOSOME™ | GSI Europe - Import + Export GmbH | Centella Asiatica Leaf Vesicles , aqua , Glycerin , Pentylene Glycol | |
| Natori Exobiome LB | Ecoori | Lactobacillus Extracellular Vesicles , Butylene Glycol , 1,2-Hexanediol | |
| ActiEV-CICA | DKSH | aqua , Butylene Glycol , 1,2-Hexanediol , Centella Asiatica Leaf Vesicles , Ethylhexylglycerin | |
| ActiEV-Brocoli | DKSH | aqua , Butylene Glycol , 1,2-Hexanediol , Brassica Oleracea Italica (Broccoli) Vesicles , Ethylhexylglycerin | |
| C-EXO | DKSH | Citrus Reticulata (Tangerine) Fruit Extract , Citrus Reticulata (Tangerine) Fruit Juice Vesicles , Glycerin , 1,2-Hexanediol |
All of the raw materials listed can be easily incorporated into exosome cosmetic products, whether as a serum, mask or light gel cream.
Conclusion: prospects for brands and formulators
Plant exosomes are the turbo couriers of cell communication and open up fascinating opportunities for skin care. Exosome cosmetic products promise visible results in a short time, as active ingredients are transported precisely to where they are needed. Plant sources avoid ethical hurdles and are in line with the zeitgeist of clean, vegan and green beauty.
For cosmetics manufacturers, the following applies: those who invest now in research, quality assurance and clean supply chains can clearly set themselves apart from the competition with exosome cosmetic products.
We have the expertise to safely formulate and stabilise exosomes and integrate them into tailor-made formulations. From anti-ageing serums to after-treatment boosters, we work with you to develop efficient, scientifically based formulations that strengthen your brand in the long term.
Because tomorrow, it’s those who cleverly use nature’s smallest messengers today who will count.
Curious?
Then send us an email at info@cosmacon.de, call us directly on +49 40 840 555 26 or fill out the contact form at www.cosmacon.de in less than two minutes.
Our formulation experts will get back to you within 24 hours with initial ideas – personal, straightforward and tailored to your brand.
Get in touch now and take the next step towards powerful skincare!
Literature:
The novel mechanisms and applications of exosomes in dermatology and cutaneous medical aesthetics.
Xiong M, Zhang Q, Hu W, Zhao C, Lv W, Yi Y, Wang Y, Tang H, Wu M, Wu Y.Pharmacol Res. 2021 Apr;166:105490
Stem cell-derived exosomes: emerging therapeutic opportunities for wound healing.
Zhou C, Zhang B, Yang Y, Jiang Q, Li T, Gong J, Tang H, Zhang Q.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023 Apr 26;14(1):107
Exosomes: The emerging mechanisms and potential clinical applications in dermatology.
Yu H, Feng H, Zeng H, Wu Y, Zhang Q, Yu J, Hou K, Wu M.Int J Biol Sci. 2024 Feb 25;20(5):1778-1795
Anti-Inflammatory microRNAs for Treating Inflammatory Skin Diseases.
Yang SC, Alalaiwe A, Lin ZC, Lin YC, Aljuffali IA, Fang JY.Biomolecules. 2022 Aug 3;12(8):1072
The therapeutic and commercial landscape of stem cell vesicles in regenerative dermatology.
Davies OG, Williams S, Goldie K.J Control Release. 2023 Jan;353:1096-1106