Collagen – a skin structure protein
Introduction
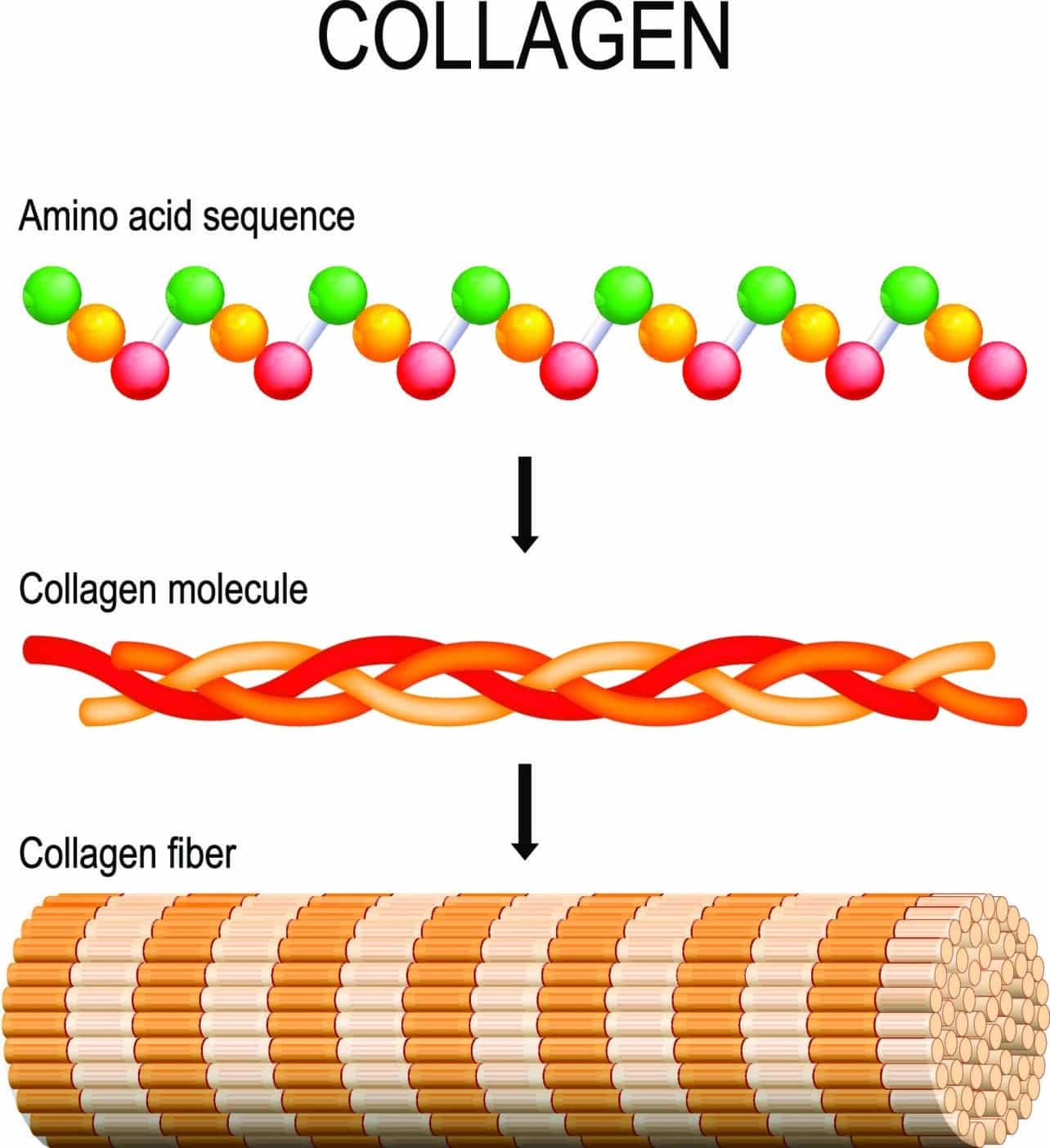
Collagen, a skin structure protein, is one of the most important building blocks of our body. It ensures the stability, elasticity and hydration of the skin and is therefore indispensable for a youthful appearance. In the dermis, collagen, a skin structure protein, forms a tear-resistant framework that not only provides structure but also serves as an interaction matrix for cells in the extracellular matrix.
With age, the collagen content of the skin decreases, causing the skin to lose volume, elasticity and moisture retention. This is precisely why this raw material is considered key in modern cosmetics.
There are different types of collagen
The collagen family currently comprises 28 known types. The following types are particularly relevant for skin care:
- Type I: Main component of the dermis, provides mechanical strength.
- Type II occurs mainly in cartilage and is important for pressure resistance.
- Type III occurs together with type I in the skin and plays an important role in wound healing.
- Type IV forms net-like structures in basement membranes.
- Type VII anchors the basement membrane to the underlying tissue.
Types I and III of collagen, a skin structure protein, are particularly important for youthful skin.
Significance in skin care products
Collagen is usually used in cosmetics in two forms:
– Native collagen with an intact triple helix structure: film-forming, highly hydrating, reduces transepidermal water loss.
– Hydrolysed collagen is broken down into peptide fragments, less water-binding, but better suited for nutritional supplements (nutricosmetics).
Native collagen, a skin structure protein, can protect, smooth and moisturise the skin’s surface. These effects are further enhanced when combined with hyaluronic acid.
Animal vs. vegan collagen
There is no such thing as genuine plant-based collagen, a skin structure protein, as collagen occurs exclusively in animal tissue. Under the label ‘vegan collagen’, there are three groups in cosmetics:
– Biotechnologically produced collagen analogues (recombinant, genetically engineered).
– Plant extracts or peptides that stimulate the body’s own collagen synthesis (collagen boosters).
– Structurally related proteins that mimic similar effects.
These products are valuable alternatives, but scientifically speaking, they are not identical to collagen.
Ideas for collagen-containing products
Hydrating serums with native collagen – a skin structure protein for immediate smoothing.
– Anti-ageing creams with combination formulas of collagen and hyaluronic acid.
– Sheet masks with film-forming collagen for intensive short-term effects.
– Nutricosmetic drinks based on hydrolysed collagen
– Lip care with collagen film formers to smooth fine lines.
Conclusion
Collagen is a central element of modern skin care. Whether in native, hydrolysed or biotechnologically mimicked form, it offers numerous starting points for innovative products. Transparent communication remains important, especially with regard to ‘vegan’ alternatives.
Cosmacon develops tailor-made formulations with collagen, a skin structure protein, from anti-ageing serums to innovative mask concepts. Contact us today to get your project started.
For those who want to get started right away, our partner Tojo Cosmetics offers ready-made private label products in the field of collagen, a skin structure protein – quickly available and ready for market.
Literature:
Collagen Supplementation for Joint Health: The Link between Composition and Scientific Knowledge.
Martínez-Puig D, Costa-Larrión E, Rubio-Rodríguez N, Gálvez-Martín P. Nutrients. 2023 Mar 8;15(6):1332
Collagen-Based Products in Wound, Skin, and Health Care.
Sen CK, Friday A, Khanna S, Roy S. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2025 Jul 28:10.1177/21621918251361118
Promoting collagen synthesis: a viable strategy to combat skin ageing.
Wang S, Li F, Feng X, Feng M, Niu X, Jiang X, Chen W, Bai R.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2025 Dec;40(1):2488821.