Spathulenol
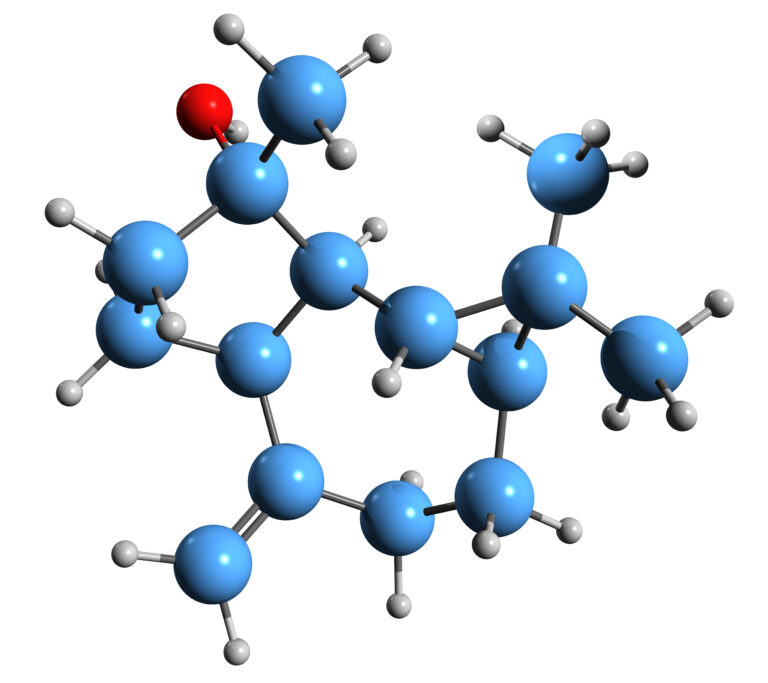
The organic chemical, low-molecular compound spathulenol is a guaiacane derivative and belongs to the group of tricyclic sesquiterpene alcohols. Its basic structure is similar to that of azulene. It occurs in plants such as German chamomile, mugwort, tarragon, anise hyssop, in cotton species and in two different St. John’s wort plants.
Extraction of spathulenol
The essential oil obtained by steam distillation of tarragon and mugwort served as the basis for the first isolation of spathulenol in 1975. The viscous and colourless compound has a bitter-spicy taste and an earthy, aromatic smell. It dissolves well in water vapour and ethanol. When dehydrated, beta-spathulenol is formed. Spathulenol should be stored at a low temperature and protected from direct sunlight.
Properties and effects
As a biologically active substance, spathulenol has an immunosuppressive effect. In the course of experiments, the death of lymphocytes has already been observed, but this is dependent on the dose. The substance has the potential to support chemotherapy during cancer treatment, which can be attributed to the inhibition of the multidrug resistance protein 1 (MDR1) in vitro. In the DPPH and MDA systems, the substance exhibits significant antioxidant activity. The IC50 value is 85.60 µg/ml.
It is said to have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-mycobacterial and anti-proliferative properties.
These properties contribute to the fact that, for example, German chamomile is still of great importance in both traditional and empirical medicine today. Even though it has been valued as a medicinal plant for centuries, experts continue to predict a great future for it. However, the possibilities and limitations have not yet been fully researched. Interest in chamomile and its ingredients, such as spathulenol, has been rapidly increasing in recent years.
For example, in 1982 there were not even 50 publications on the subject worldwide, but by 2001 this number had tripled. It is a fact that the therapeutically interesting ingredients are largely found in the essential oil. This is obtained by steam distillation from the flowers of the camomile.
The proportion of spathulenol is about one per cent. In addition, the bisabolides, spiroethers and azulenes are particularly worthy of mention. Of course, there are also many other lipophilic and hydrophilic substances in chamomile. Examples include flavonoids such as apigenin, coumarins, polysaccharides, amino acids, phytosterols and mineral components. As already mentioned, the studies are far from over, and there is still a great deal to be researched about the azulenogenic tricyclic sesquiterpene alcohol spathulenol. A study published a few years ago can be read here: It is true that this study is about Psidium guineense Sw., a type of guava, but spathulenol is one of its main components and its leaves have been successfully used in folk medicine for a very long time to treat inflammations. However, before this study, there was no evidence of its actual effectiveness. The study results were able to prove this, though.
Spathulenol in skin care
In any case, it is a fact that chamomile also plays an important role in skin care, not least thanks to its active ingredient spathulenol, because its antioxidant, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties cannot be denied. Using it, for example, helps irritated, stressed or sensitive skin to relax better. This can be the case with redness and itching, but also with tight and dry skin as well as acne.
Spathulenol: a brief profile
INCI: Spathulenol
CAS number: 6750-60-3
Appearance: colourless to light yellow
Alternative names: (1aR,4aR,7S,7aR,7bR)-1,1,7-Trimethyl-4-methylidene-1a,2,3,4a,5,6,7a,7b-octahydrocyclopropa[h]azulen-7-ol, Espatulenol
Boiling point: 269 to 270 degrees Celsius
Molecular formula: C15H24O
Molar mass: 220.356 (g/mol)
Effect: antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-proliferative and anti-mycobacterial
Spathulenol: an important constituent with interesting benefits
The guaiacane derivative, which occurs in plants such as German chamomile and St. John’s wort, has not yet been fully researched, but studies have already shown some of its effects. Its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties are particularly interesting for use in cosmetics. There are good reasons why chamomile is used to sooth and care for irritated, stressed and blemished skin. Would you like to offer your target group high-quality cosmetics with spathulenol? We are always at your disposal.
Literature: