Honokiol and magnolol: the dual power of magnolia bark
Introduction
The search for natural active ingredients that combat skin problems gently but effectively continues to yield fascinating results. Two of the most exciting examples are honokiol and magnolol, two bioactive compounds found in the bark of Magnolia officinalis.
Both are considered key substances for anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and antimicrobial effects and are increasingly found in modern cosmetic products.
In this article, you will learn everything about the origin, effects, uses and chemical properties of honokiol and magnolol – a natural power duo for healthy, beautiful skin.
Origin and extraction
Honokiol and magnolol are derived from the bark of the Asian magnolia tree (Magnolia officinalis), which grows in China, Korea and Japan. The bark is traditionally used in Chinese medicine and is known for its soothing and anti-inflammatory properties.
For cosmetic use, honokiol and magnolol are isolated from the dried bark by ethanol extraction or CO₂ extraction. Together, they make up to 98% of the total active ingredient content of a high-quality magnolia extract.
Mode of action in skin care
Anti-inflammatory
Both honokiol and magnolol specifically inhibit the pro-inflammatory signalling pathway around the transcription factor NF-κB, thereby suppressing the release of cytokines such as IL-6 and TNF-α, which cause redness, swelling and skin ageing.
Antioxidant properties
Free radicals (ROS), which are produced by UV radiation or environmental pollution, for example, attack cell structures and accelerate skin ageing. Honokiol and magnolol act as effective radical scavengers, protecting collagen and elastin in the connective tissue.
Antimicrobial effect
Both substances are effective against bacteria that cause acne and skin infections, such as Staphylococcus aureus and Propionibacterium acnes. They also inhibit the growth of Streptococcus mutans in the oral cavity, helping to reduce tooth decay and bad breath.
Applications in cosmetic products
Honokiol and magnolol are ideal for the following types of products:
- Anti-ageing creams
- Acne care products
- Soothing care for couperose or rosacea
- After-sun products
- Dental and oral care
Formulations with liposomes or water-dispersible carrier systems have proven particularly effective, as they enable better skin availability (e.g. MAXnolia from Mibelle Biochemistry).
Active ingredients in detail
Honokiol
Appearance: White to yellowish powder
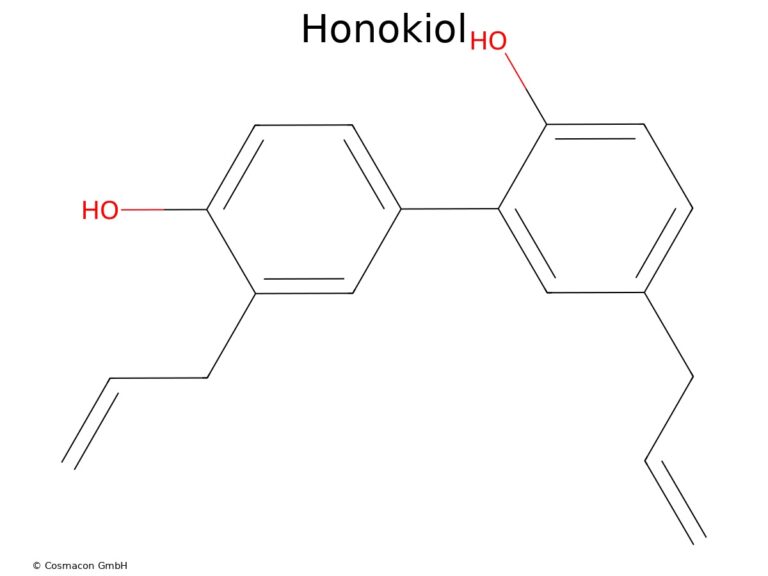
Molecular formula: C18H18O2
Molar mass: 266.33 g/mol
Melting point: approx. 86–88 °C
Solubility: Soluble in ethanol, poorly soluble in water
Effect: Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, anxiolytic
INCI name: Honokiol
Use: Anti-ageing, anti-acne, soothing care
Magnolol
Appearance: White powder
Molecular formula: C18H18O2
Molar mass: 266.33 g/mol
Melting point: approx. 102–106 °C
Solubility: Soluble in ethanol, poorly soluble in water
Effect: Anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antioxidant, anti-allergic
INCI name: Magnolol
Use: Skin care, oral care, after-sun products
Study
A study with gingival cells showed that honokiol and magnolol significantly reduce the production of IL-6 and MMP-9.
- Another study demonstrated their effectiveness against periodontal pathogens and skin germs with a minimum inhibitory concentration of 25 µg/ml.
- In vivo tests with chewing gum showed that honokiol and magnolol can reduce the oral bacterial load by over 60%.
We enjoy working with these magnolia extracts containing honokiol and magnolol:
Conclusion
Honokiol and magnolol offer an outstanding combination of skin-soothing, protective and regenerative effects. Their diverse properties make them ideal active ingredients for modern, natural skin care products. They offer visible improvements, especially for sensitive, mature or inflamed skin.
With the right technologies, such as liposomes or water-soluble carriers, Cosmacon GmbH can integrate these two active ingredients into highly effective cosmetic products. This not only strengthens the skin health of your customers, but also the innovative power of your brand.
Please feel free to contact us – we will be happy to advise you.
Literature:
Safety and Toxicology of Magnolol and Honokiol.
Sarrica A, Kirika N, Romeo M, Salmona M, Diomede L.Planta Med. 2018 Nov;84(16):1151-1164
Chiu KC, Shih YH, Wang TH, Lan WC, Li PJ, Jhuang HS, Hsia SM, Shen YW, Yuan-Chien Chen M, Shieh TM.J Formos Med Assoc. 2021 Feb;120(2):827-837
Lovecká P, Svobodová A, Macůrková A, Vrchotová B, Demnerová K, Wimmer Z.Plants (Basel). 2020 Jul 11;9(7):879